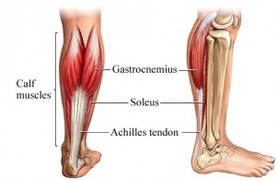
See Pic
The Gastrocnemius functions in quick movements in the leg such as running and jumping while the soleus initiates more when still or in a stance position. The gastrocnemius muscle is prone to muscle cramping and spasms. These are involuntary and may last several seconds to minutes. Often, amongst women who wear high heel shoes, the calf muscles stay shortened for long periods of time and may eventually accommodate its new length by shortening and becoming tight. Another issue is inflammation of the gastrocnemius commonly caused by overuse injuries. This pain and inflammation can be helped by oral anti-inflammatories, stretching, massage, myofascial or muscle release, heat therapy, topical anti-inflammatories to name a few. Below I will discuss two of these treatments; Stretching and Myofascial (Muscle) release techniques.
Stretching:
Lets go over a few basic stretching techniques. The first is static stretching.
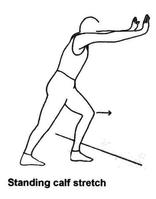
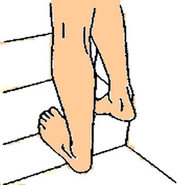
Static Stretching is the most common type of stretching. You all have most likely performed this type of stretching before. Basically, this is a stretch that is held in a position that is somewhat comfortable but at the same time challenging for a period of time usually 10-30 seconds. Many experts believe that static stretching is not as beneficial for improving range of motion and function as compared to dynamic stretching.
Dynamic Stretching is when you repeatedly move through a comfortable but challenging range of motion stretch. This occurs approximately 10-12 times. You must repeat these moves in a controlled, smooth and deliberate fashion.
Hold-Relax Stretching aka a type of PNF Stretching (proprioceptive muscular facilitation) can be both passive or active. Hold-relax stretching specifically is performed by contracting or holding and passive stretching or relaxing. PNF stretching usually involves a 10 second push phase followed by a 10 second relaxation phase, typically repeated a few times. These types of stretches involve a partner actively stretching the participant by some combination of altering contraction and relaxation of both agonist and antagonist muscle groups. An advantage of PNF stretching is the possibility of producing greater improvement in flexibility compared to other techniques. Its disadvantage is that, it typically requires a partner. So grab a partner to work with, this can be a motivation booster!
There was a recent study performed in the Journal of Sport Rehabilitation 2015 by Nakamura et al that showed there is indeed a difference between static stretching and hold-relax stretching. The results showed that end range of motion (ROM) and passive torque at the end ROM significantly increased immediately after both hold-relax stretching and static stretching, whereas muscle stiffness significantly decreased. In addition, the percent change in passive torque at end ROM upon use of the hold-relax stretching technique was significantly higher than that after use of the static stretching technique. However, the percent change in muscle stiffness following static stretching was significantly higher than that with hold-relax stretching. Basically, they suggested that both hold-relax stretching and static stretching can effectively decrease muscle stiffness of the gastrocnemius. In addition, these results suggest that hold-relax stretching induces a change in the passive torque at end ROM, i.e., sensory perception, rather than changing muscle stiffness.











 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

